COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) and emphysema are terms that are often used together, so it can be hard to tell if there is a difference between the two.
What is COPD? What is Emphysema?
COPD is an umbrella term for various lung diseases that make it difficult to breathe. If someone has COPD, they could have one or more of the conditions that fall under this term.
Emphysema is a severe form of COPD. It happens when the air sacs in the lung, called alveoli, are damaged by things like smoking or air pollution. This damage makes it harder for the lungs to exchange air, trapping old air inside and preventing new air from entering. The trapped air causes hyperinflation, where the lung expands and puts pressure on the diaphragm, making breathing take more effort.
Causes and Symptoms
A range of factors can contribute to the development of COPD and emphysema, with smoking being a common cause. However, exposure to secondhand smoke, pollutants, chemical fumes, lung irritants, or a genetic disorder called alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can also play a role. This genetic disorder affects a specific protein in the body, which can increase the risk of developing COPD and emphysema.
Because emphysema is a type of COPD, the two share similar symptoms. These can include:1
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea), especially during physical activity
- Coughing
- Fatigue
- Weight Loss
Some symptoms are common across types of COPD, but different forms of COPD may also have their own specific symptoms because of how they impact the lungs in different ways.2
Relieving COPD/Emphysema Symptoms
Along with medication, surgery, and other treatment options, there are some lifestyle changes that can help individuals with their COPD/Emphysema symptoms. These include:3
- Exercise and physical activity, which can improve lung function and strength
- Maintaining a healthy diet, which helps keep the body and immune system strong
- Quitting smoking, which can slow the progression of the disease
Treatment for COPD/Emphysema
While there is no cure for COPD and emphysema, treatments can help slow down disease progression, relieve symptoms, and improve quality of life. Treatment options range from non-invasive approaches like, inhalers, oxygen therapy, and pulmonary rehabilitation, to more invasive interventions such as lung volume reduction surgery and lung transplants. For severe COPD/emphysema, there is also a minimally invasive treatment option called the Zephyr® Valve.
Links:
US-EN-1910-v1






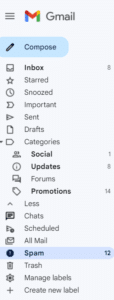
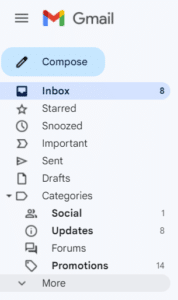 If you do not see an email from “Val at Zephyr Valve” in your inbox within 15 minutes of signing up, go to your “Spam” folder within Gmail. (You may have to click "More" to see the Spam folder.) Select the email from "Val at Zephyr Valve."
There will be a gray box at the top that says “Why is this message in spam?” Click the “Report Not Spam” button. This will move the email to your inbox.
If you do not see an email from “Val at Zephyr Valve” in your inbox within 15 minutes of signing up, go to your “Spam” folder within Gmail. (You may have to click "More" to see the Spam folder.) Select the email from "Val at Zephyr Valve."
There will be a gray box at the top that says “Why is this message in spam?” Click the “Report Not Spam” button. This will move the email to your inbox.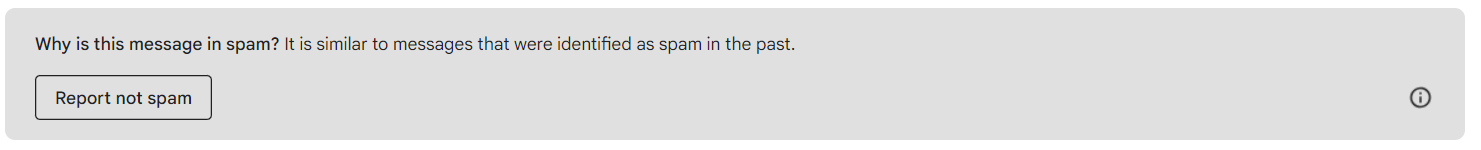 Go back to your inbox and open the email. Click on the icon next to “Val at Zephyr Valve”, you’ll see a person icon with a “+”. Click that, and you can add Val to your Contacts list. If you don’t receive a second email from us in a few days, please check your Spam folder again.
Go back to your inbox and open the email. Click on the icon next to “Val at Zephyr Valve”, you’ll see a person icon with a “+”. Click that, and you can add Val to your Contacts list. If you don’t receive a second email from us in a few days, please check your Spam folder again.
